MS Thesis Defense, Zeerak Ajmal
Title: Deep learning-based surface area calculation for 3D point cloud registration with a synthetic terrain dataset
MS Thesis Defense: Zeerak Ajmal, Student of MS Data Science, IBA Karachi
Advisor: Dr. Faisal Iradat
External Examiners: Dr. Taslim Murad (IBA-SMCS) | Dr. Umar Farooq (NED University)
Date: January 28, 2026, at 09:00AM
Venue:
Tabba Conference Room, Tabba Academic Block, Second Floor [North Wing], Main Campus, IBA Karachi
Abstract
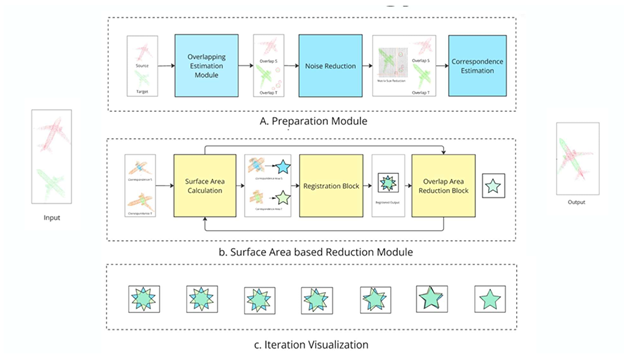
Point cloud registration remains a challenging problem in computer vision and remote sensing due to sparsity, noise, and the lack of reliable global geometric cues. Existing methods largely depend on local correspondences and iterative optimization, which are sensitive to initialization and computationally expensive. Additionally, most real-world point cloud datasets do not provide ground-truth surface area information, limiting the use of surface-based geometric constraints. This research proposes a Surface Area–based Reduction Module (SARM) that introduces surface area as a global geometric feature to support point cloud registration. A large-scale synthetic terrain dataset containing over 200,000 point cloud samples was generated, representing diverse natural landscapes, with accurate surface area ground truth obtained through mesh-based triangulation. Several deep learning models were evaluated for surface area estimation, including voxel-based 3D CNNs, PointCNN, DGCNN, and PointNet++. Experimental results show that PointNet++ achieves the best performance, benefiting from hierarchical feature learning and multi-scale neighborhood aggregation. The proposed framework attains an RMSE of 4.76%, demonstrating robust and accurate surface area estimation across varying terrain types. The results confirm the effectiveness of SARM and highlight its potential for improving point cloud registration and related applications in terrain analysis and remote sensing.